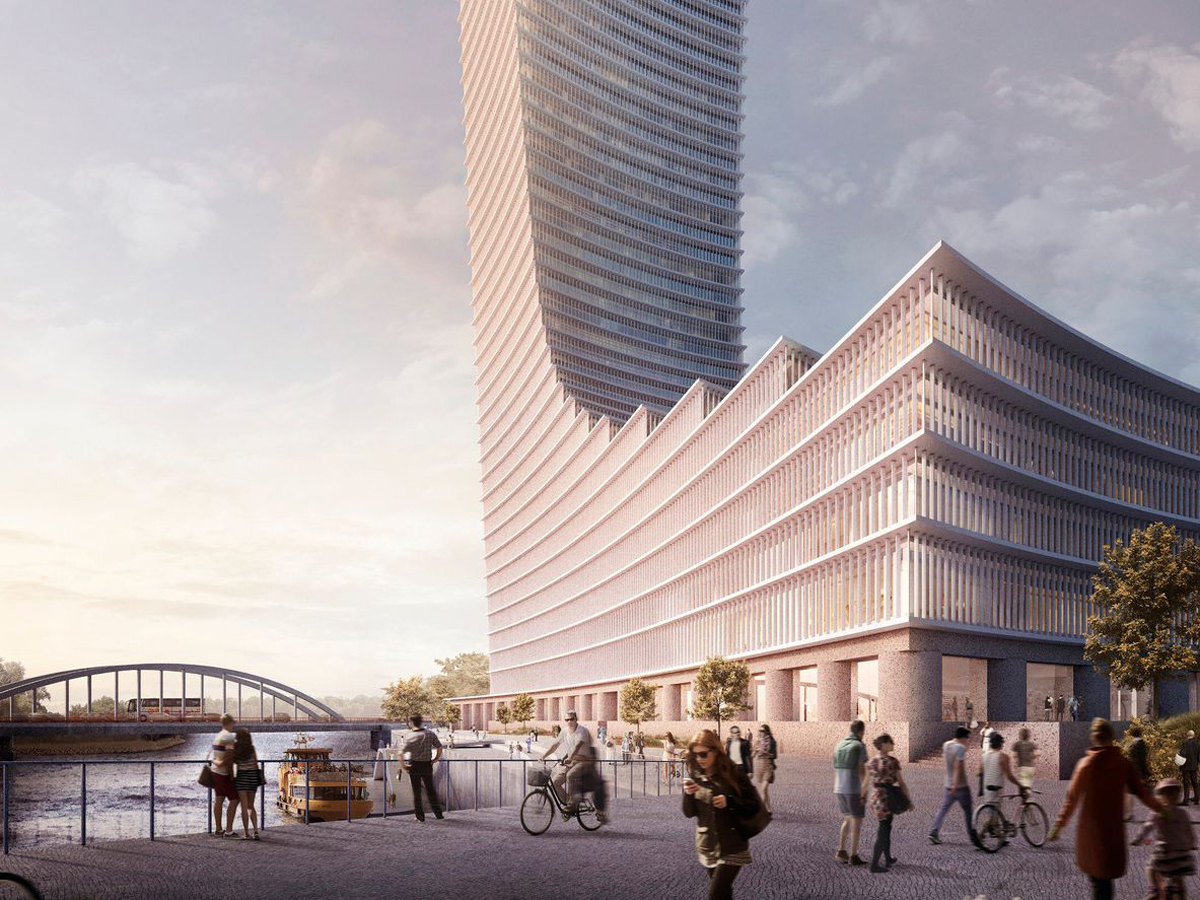
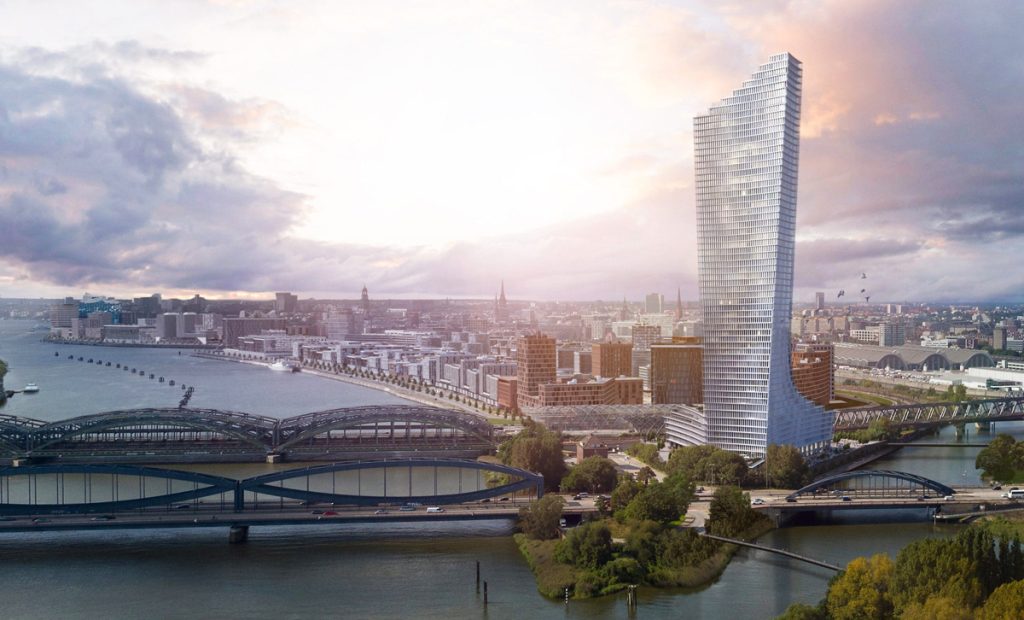
Rising on the eastern tip of Hamburg’s HafenCity, the Elbtower was envisioned as a defining vertical landmark for the city’s evolving waterfront. Designed by David Chipperfield Architects, the tower was meant to symbolize Hamburg’s fusion of maritime heritage and modern urban ambition. Planned as the tallest structure in the city and among the tallest in Germany, the Elbtower represents both promise and pause—a statement of architectural aspiration and a mirror of market uncertainty.
Vision & Strategic Positioning
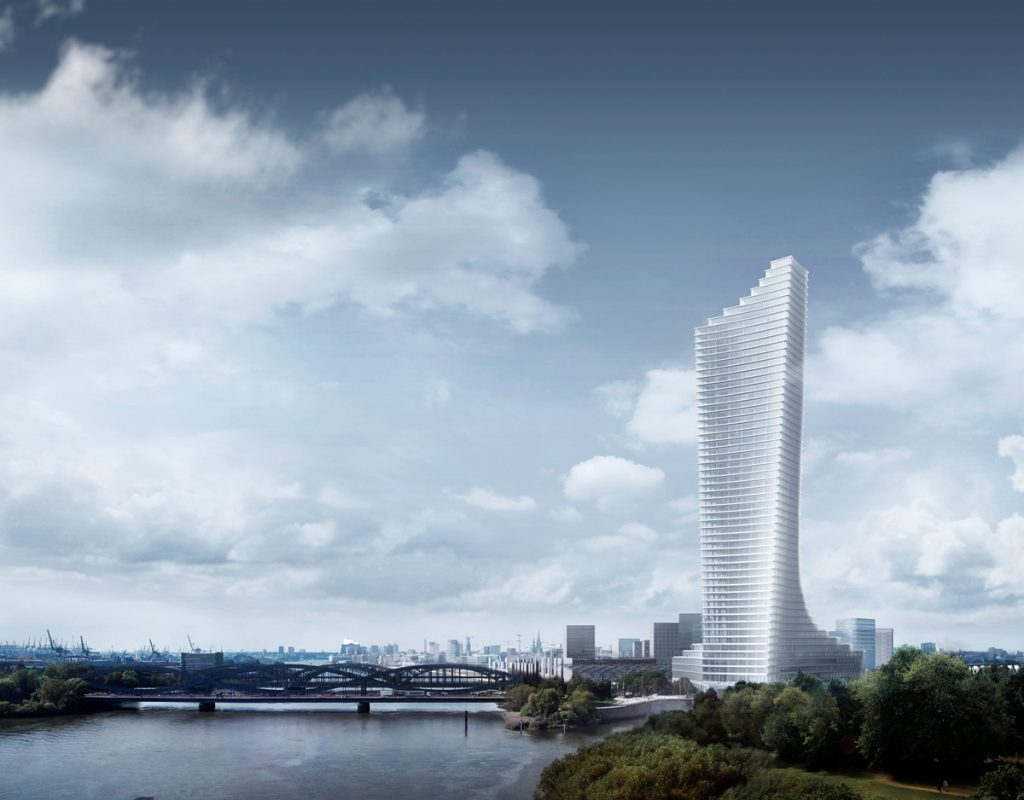

The Elbtower’s design aimed to create a sculptural counterpoint to the Elbphilharmonie on the opposite side of HafenCity, framing the city’s river gateway with two architectural icons. Positioned at the intersection of the Elbe River and Oberhafen Canal, it was conceived as the eastern anchor of the HafenCity development—an entry marker visible from air, land, and water.
- Intended as a symbolic “gateway” to Hamburg’s expanding waterfront
- Strategically located beside the Elbbrücken transport hub
- Planned as a commercial, cultural, and hospitality centerpiece for the district
Master Plan & Core Components
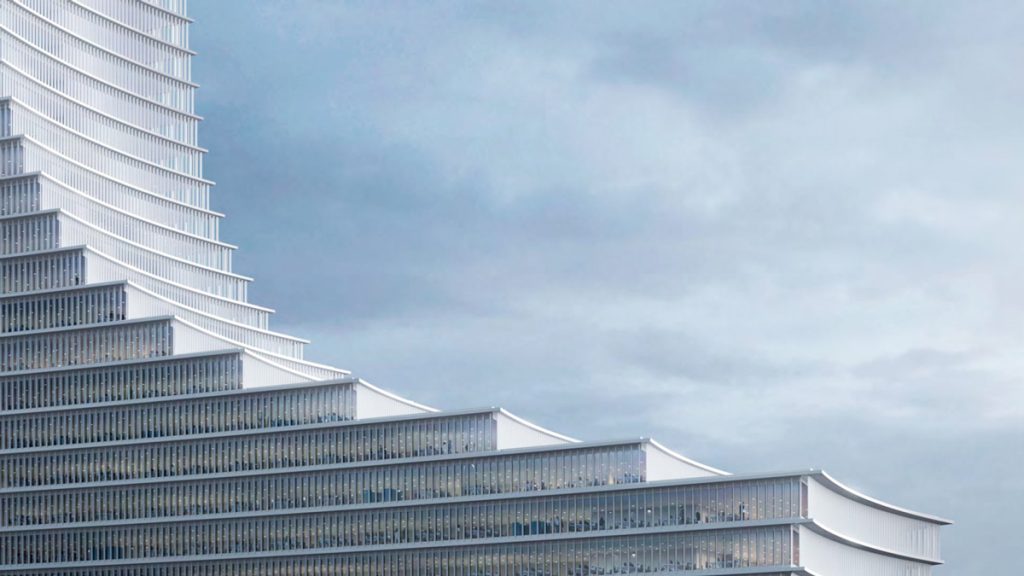

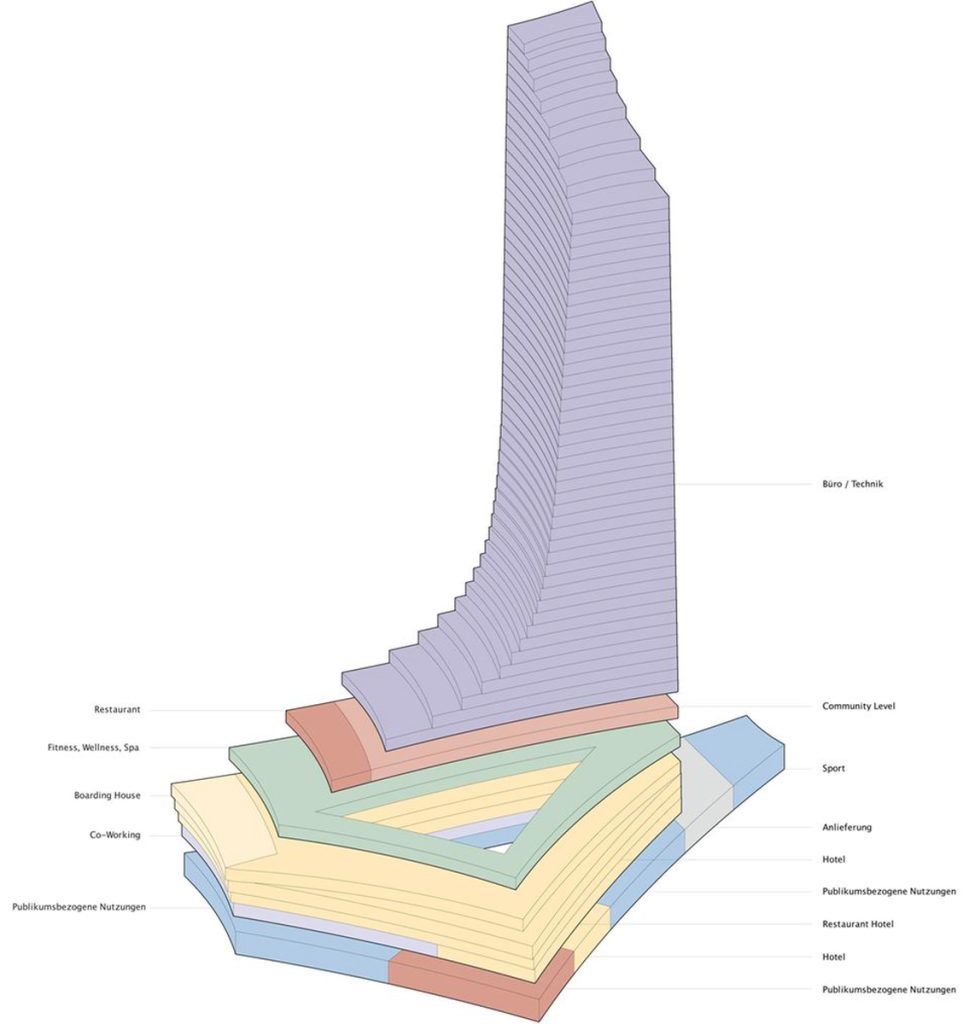
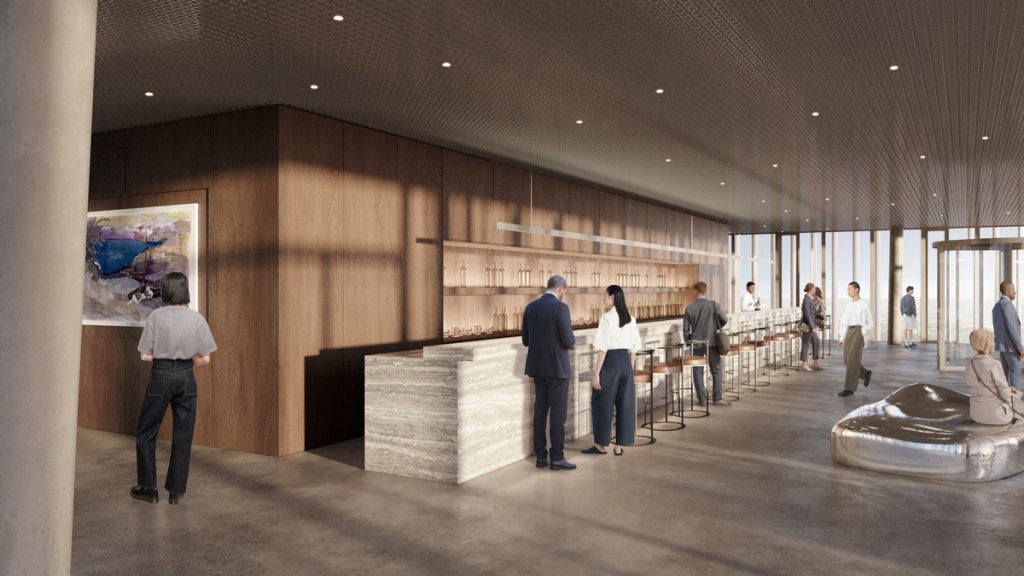
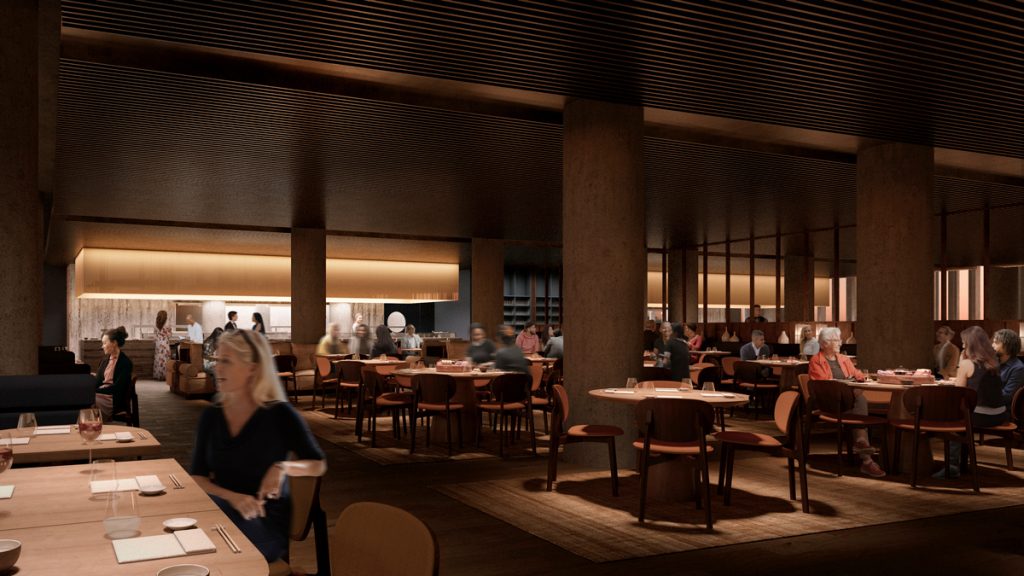
The project features a mixed-use composition combining public, commercial, and leisure spaces within an elegant tapering tower above a multi-level podium.
- Height: Approximately 245 meters, with 64 floors
- Podium: About 13,000 m² of retail, dining, and event space
- Tower: Office floors, a luxury hotel, and panoramic viewing areas
- Public Features: A central atrium and terrace connecting to riverfront pathways
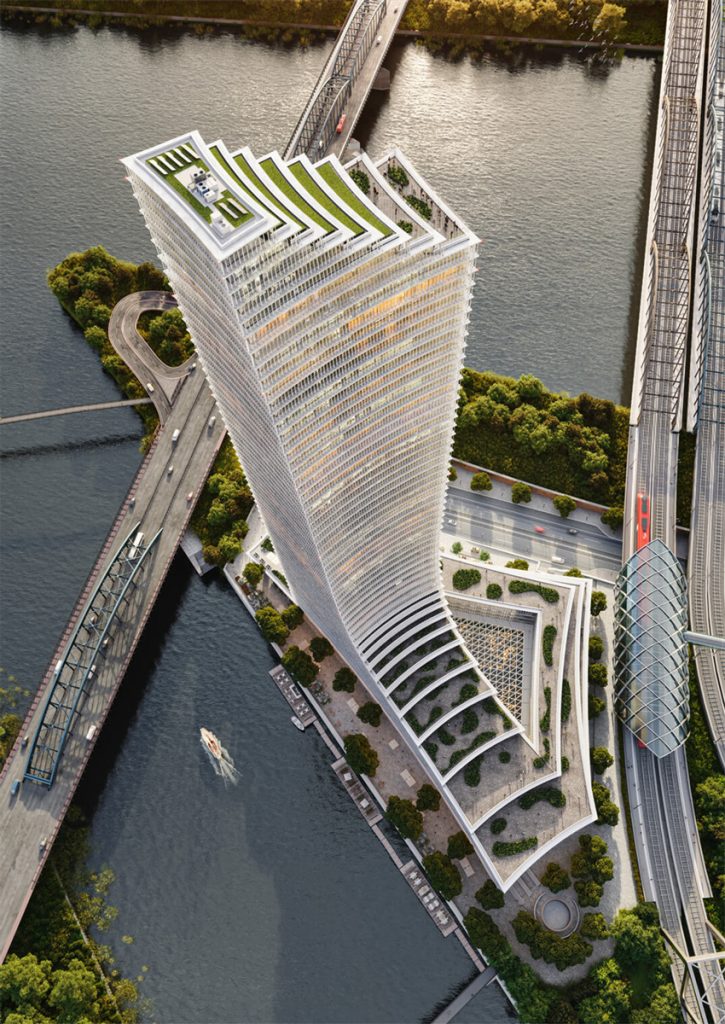

The developer, SIGNA Prime Selection AG, led the investment initiative, while David Chipperfield Architects guided the design alongside structural engineers wh-p Ingenieure. The scheme’s integration with Hamburg’s transport systems—including direct access to the Elbbrücken S-Bahn and U-Bahn stations—was planned to ensure pedestrian permeability and strong civic presence.
Development & Investment Potential
Elbtower was designed to strengthen Hamburg’s international profile by anchoring new commercial and leisure demand in HafenCity’s east. The tower’s mix of high-end office spaces, hotel amenities, and premium retail made it a high-value asset in Germany’s real estate portfolio.
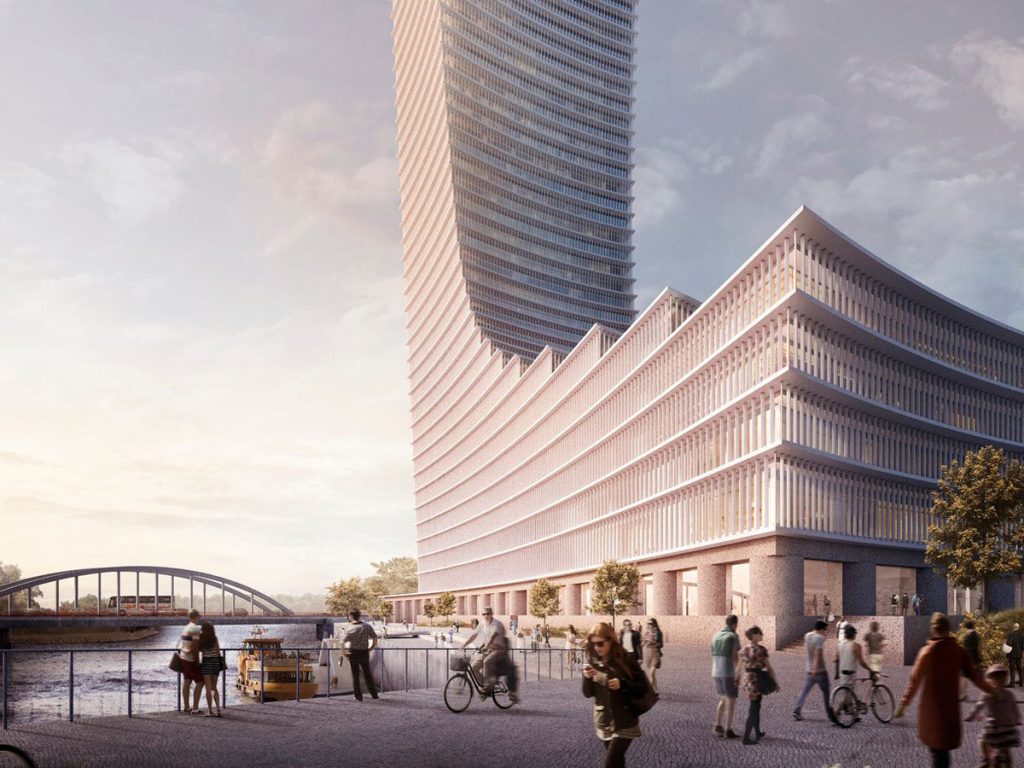

- Prime Class-A office space in a growing innovation corridor
- Strong tourism and brand appeal due to architectural prominence
- Anticipated economic uplift for the Grasbrook and Billebogen zones
At full completion, the Elbtower would have positioned Hamburg alongside cities like London and Paris in hosting a modern mixed-use high-rise of international caliber.
Sustainability & Innovation
The design’s structural fluidity and tapering form were intended to reflect the movement of the river while ensuring engineering efficiency.
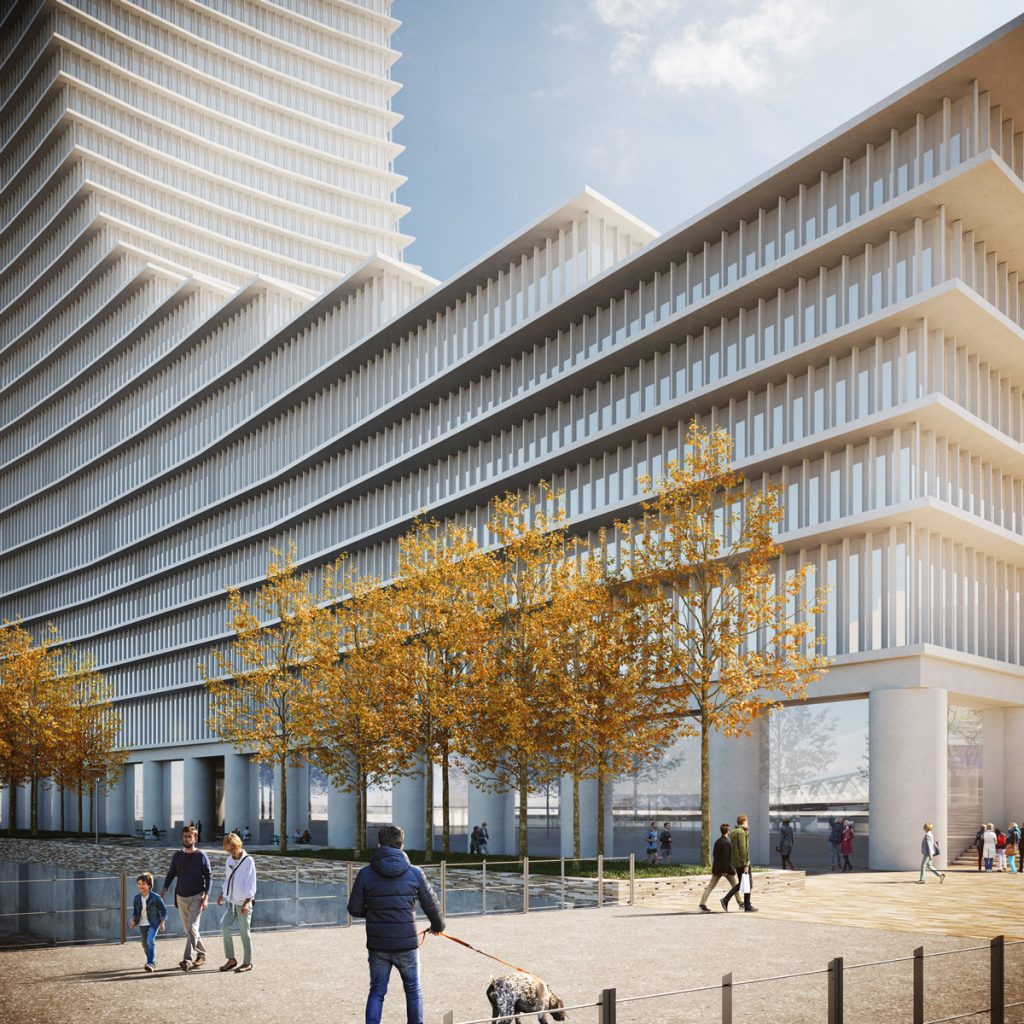


- Dynamic floorplate geometry reducing wind load and mass perception
- High-performance façades designed to optimize daylight and energy use
- Integration with HafenCity’s wider sustainable urban guidelines
- Use of advanced concrete and steel composites to minimize material weight
Sustainability in the Elbtower’s concept extended beyond structure—envisioning an active, accessible civic landmark with a low environmental footprint for its scale.
Challenges & Considerations
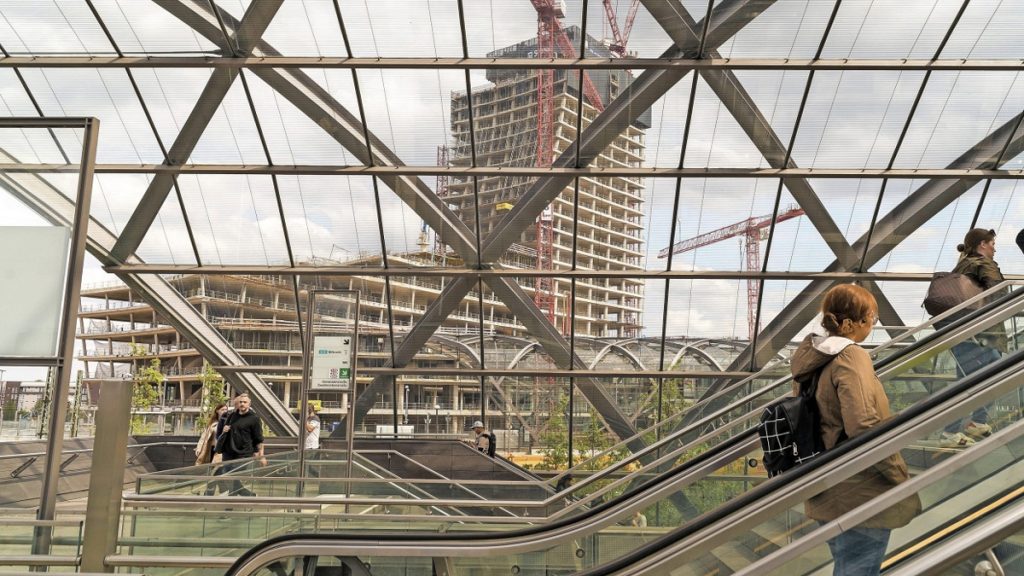
Despite its vision, the Elbtower has faced substantial difficulties. Construction began in 2021 but was halted in late 2023 due to financial complications involving the developer’s parent company.


- Developer insolvency and unresolved contractor payments halted progress
- Cost escalation nearing €950 million increased investment risk
- Engineering challenges related to foundation settlement and proximity to rail lines
- Broader market pressures on office leasing post-pandemic affected viability
As of 2025, the structure remains incomplete—its future hinging on new capital infusion or public-private restructuring.
Urban Impact & Legacy

Even in its suspended state, the Elbtower stands as a symbol of Hamburg’s architectural ambition and evolving skyline identity. When realized, it could extend HafenCity’s footprint eastward, catalyzing new development clusters and reinforcing Hamburg’s image as a forward-looking global city.
Yet its current limbo underscores the fragility of large-scale speculative projects in Europe’s changing urban economy. Whether completed or reimagined, Elbtower’s legacy will continue to influence how Hamburg balances bold design with market realism.
Summary
The Elbtower remains one of Germany’s most audacious development ventures—a sleek, mixed-use high-rise intended to redefine Hamburg’s skyline. Combining world-class architecture, civic aspiration, and complex financial realities, the tower encapsulates the dual nature of modern urban progress: visionary yet vulnerable. Its outcome will determine whether it becomes Hamburg’s next great landmark—or a monument to unfulfilled ambition.

Project Facts & Figures
- Location: HafenCity, Hamburg, Germany
- Height: Approx. 245 m (64 floors)
- Use: Mixed-use (offices, hotel, retail, public spaces)
- Developer: SIGNA Prime Selection AG
- Architect: David Chipperfield Architects
- Structural Engineers: wh-p Ingenieure
- Estimated Cost: €950 million
- Construction: Began 2021; halted 2023
- Status: On hold pending new investors or restructuring




